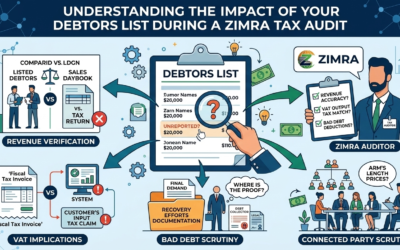
Is a Trust Taxable in Zimbabwe?
Generally a trust is not taxable under the Zimbabwe tax system. An exception, however, is when it has income to which no beneficiary is entitled.
When are Trust Taxed?
The taxation of trusts and beneficiaries emanates from the Section 2 and 10 of the Act. Section 2 of the Act provides that trust is only a person when it has income the subject of which no beneficiaries is entitled to.
Only persons are taxable under Income Tax, the trust will be taxable on trust income, the subject of which no beneficiaries are entitled to. The beneficiaries that will be taxed are those that have vested right or whom income has been distributed. The trust will pay tax on undistributed trust income or on income not derived for immediate or future benefit of an ascertained beneficiary.
A definition in Section 2 of the income tax act stresses that “person” includes a company, body of persons corporate or unincorporate (not being a partnership), local or like authority, deceased or insolvent estate and, in relation to income the subject of a trust to which no beneficiary is entitled, the trust.
Section 10(1) of the the Income Tax, deems income to have been accrued or received by a person irrespective of such income having been invested, accumulated or otherwise capitalised by the person. Thus, income can be taxed in the hands of a beneficiary nonwithstanding such income has no actually been received by the person.
Trusts are taxed in Zimbabwe in accordance with the Income Tax Act [Chapter 23:04]. The Act provides that trusts are taxed on their income, regardless of whether the income is distributed to the beneficiaries or not. The rate of tax for trusts is the same as the rate of tax for individuals.
There are a few exceptions to the general rule that trusts are taxed on their income. For example, trusts that are established for charitable purposes are not taxed on their income. Additionally, trusts that are established for the benefit of minors are taxed at a lower rate than trusts that are established for the benefit of adults.
The trustees of a trust are responsible for filing tax returns for the trust. The trustees must file a tax return for the trust on an annual basis. The tax return must include information on the trust’s income, expenses, and distributions to beneficiaries.
If you are a trustee of a trust, it is important to be aware of the tax implications of your role. You should consult with a tax advisor to ensure that you are filing your tax returns correctly and that you are not paying more tax than you are required to.
Here are some additional details on the taxation of trusts in Zimbabwe:
- Trusts are taxed on their income, regardless of whether the income is distributed to the beneficiaries or not.
- The rate of tax for trusts is the same as the rate of tax for individuals.
- There are a few exceptions to the general rule that trusts are taxed on their income, such as trusts that are established for charitable purposes.
- Trusts that are established for the benefit of minors are taxed at a lower rate than trusts that are established for the benefit of adults.
- The trustees of a trust are responsible for filing tax returns for the trust.
- The tax return for a trust must be filed on an annual basis.
- The tax return must include information on the trust’s income, expenses, and distributions to beneficiaries.
If you are a trustee of a trust, it is important to be aware of the tax implications of your role. You should consult with a tax advisor to ensure that you are filing your tax returns correctly and that you are not paying more tax than you are required to.